Are you looking to improve your cooking skills but unsure which oil to use in your favorite recipes? Don’t worry; we’ve got you covered.
In this blog post, we delve into the ultimate showdown between sunflower oil vs vegetable oil. By exploring the differences in their sources, cooking methods, and flavor profiles, you’ll be equipped to make the best choice for your culinary creations. Let’s dive in and discover which oil reigns supreme in the kitchen!
Sunflower Oil: A Versatile and Nutritious Choice
Sunflower oil is a popular cooking oil with a long history of use. Extracted from sunflower seeds through pressing and refining, this oil is known for its lightness, mild flavor, and adaptability in the kitchen.
High Smoke Point for Versatile Cooking
One of the key benefits of sunflower oil is its high smoke point. This means the oil can reach high temperatures without burning, making it ideal for frying, sautéing, and even baking.
Packed with Health Benefits
Beyond its culinary applications, sunflower oil offers surprising nutrition. It’s rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which promote heart health and healthy cholesterol levels. Sunflower oil is also a great source of vitamin E, an antioxidant that protects cells from damage and strengthens the immune system. Additionally, it boasts omega-6 fatty acids, which are important for brain function and healthy skin. Including sunflower oil in your diet can provide a significant boost of essential nutrients and contribute to overall well-being.
A Kitchen Staple for Many Reasons
Sunflower oil’s versatility makes it a favorite among cooks. Its mild flavor and high smoking point allow it to be used in sautéing, frying, and baking. It can also be used as a base for salad dressings or marinades, adding a subtle nutty taste. Because of its neutral flavor, sunflower oil is perfect for preserving the natural flavors of delicate dishes. It’s also useful for making homemade mayonnaise or substituting for butter or vegetable oil in recipes. Thanks to its wide range of uses, sunflower oil has become a staple in many kitchens around the world.
Vegetable Oil: A Versatile Kitchen Staple

Vegetable oil is a popular cooking ingredient prized for its versatility and neutral flavor. It’s often a blend of soybeans, canola, corn, sunflower, and palm, making it a cost-effective choice.
Vegetable oil’s high smoke point makes it ideal for frying, baking, and sautéing. It’s also a common ingredient in processed foods, salad dressings, and marinades. But it’s important to remember that not all vegetable oils are the same.
Different Types, Different Benefits
There are many types of vegetable oil, each with its plant source. Here are some common ones:
- Soybean oil: The most popular, known for its neutral flavor and versatility.
- Canola oil: Low in saturated fat, making it a good option for frying and baking.
- Corn oil: Mild-tasting, suitable for sautéing and baking.
- Sunflower oil: Extracted from sunflower seeds, commonly used in dressings and marinades.
- Palm oil: Derived from the oil palm tree, used in various food products.
Each type has its own unique flavor, smoke point, and nutritional profile. Choosing the right oil depends on your cooking needs and preferences.
Vegetable Oil and Your Health
Vegetable oil is a staple for cooking and baking, but its health effects are debated. While it’s a good source of polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are essential for the body and potentially lower bad cholesterol, it’s also high in omega-6 fatty acids. Consumed in excess, omega-6s can contribute to inflammation.
Therefore, moderation is key. Consider alternatives like olive oil or avocado oil for a more balanced fatty acid profile.
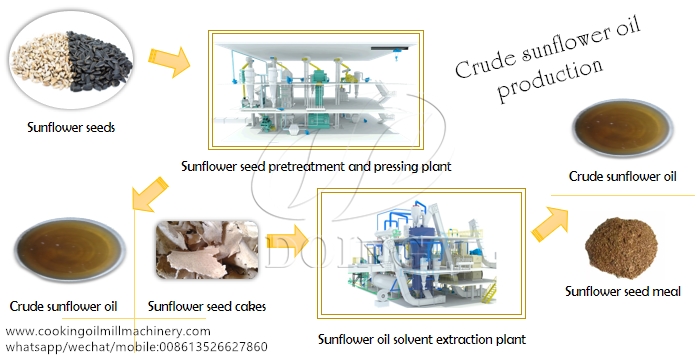
Sunflower Oil Processing: From Seed to Shelf
Sunflower oil goes through a journey before reaching your kitchen. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
Cleaning the Seeds:
The first step is cleaning the sunflower seeds. This removes dirt, debris, and any unwanted materials that might affect the oil’s quality.
Oil Extraction:
There are two main methods to extract oil from the seeds:
- Mechanical Pressing: This traditional method involves cleaning, heating, and cracking the seeds. Then, a press squeezes out the oil. It’s simpler but yields less oil.
- Solvent Extraction: Here, the seeds are crushed and mixed with a solvent (often hexane) to dissolve the oil. The solvent is then separated through evaporation and distillation. This method is more efficient but may involve chemicals.
Refining the Oil:
The crude oil needs further processing to become the clear, light-colored oil you know. This refining process removes impurities and improves its quality for cooking:
- Degumming: This removes water-based impurities.
- Neutralization: This neutralizes free fatty acids to enhance stability and prevent spoilage.
- Bleaching: This uses activated carbon or clay to remove color and any remaining impurities, resulting in a lighter oil.
- Deodorization: This step removes unwanted odors, leaving a neutral-tasting oil ideal for cooking.
The Final Product:
After refining, sunflower oil is a clear, light yellow oil with a mild flavor. This versatility makes it a popular choice for various culinary applications.
Vegetable Oil Processing: From Plant to Plate
Vegetable oil goes through a fascinating journey before it reaches your kitchen. Let’s explore the different steps involved in this process:
1. Seed Preparation:
The journey starts with the raw materials, such as soybeans, canola seeds, or corn kernels. These are thoroughly cleaned to remove dirt and debris. Depending on the source, they may also be dried and dehulled (the outer shell removed).
2. Oil Extraction:
There are two main methods for extracting oil from the seeds:
- Mechanical Pressing: This traditional method involves crushing the seeds and then applying pressure using an expeller press to separate the oil.
- Solvent Extraction: This method uses a solvent, typically hexane, to dissolve the oil from the plant material. The solvent is then evaporated, leaving behind the pure oil.
3. Refining the Oil:
The crude oil extracted from the seeds still contains impurities. Refining removes these impurities to improve the oil’s quality, taste, and shelf life. Here’s what happens during refining:
- Degumming: This process removes phospholipids and other unwanted gum-like substances.
- Neutralization: Free fatty acids, which can affect taste and odor, are neutralized using an alkali solution.
- Bleaching: Activated carbon or clay is used to remove pigments and improve the oil’s color.
- Deodorization: This final step removes any lingering odors and flavors, resulting in a clear, neutral-tasting oil perfect for cooking and other uses.
By following these steps, vegetable oil processors transform raw plant materials into the versatile cooking oil used in countless dishes around the world.
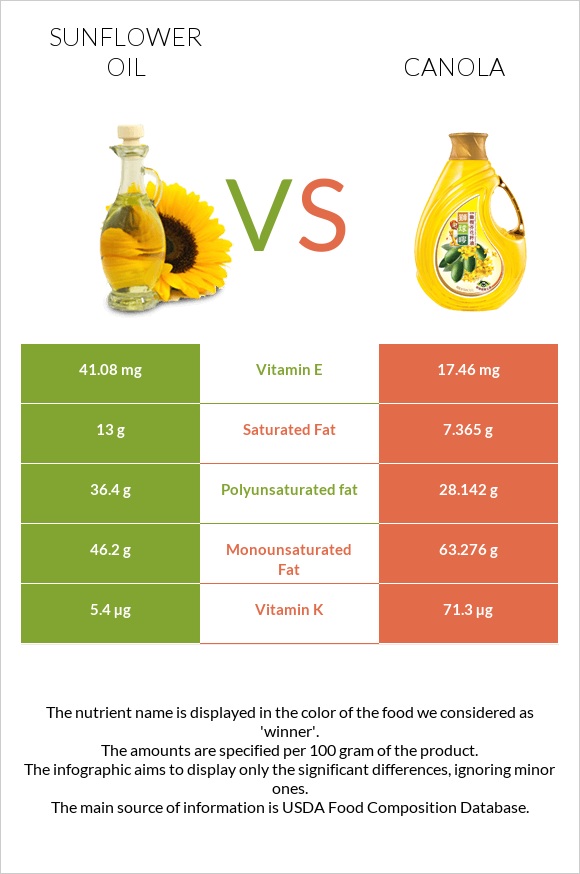
Sunflower Oil vs. Vegetable Oil: A Nutritional Breakdown
Wondering which oil to choose for your cooking? Both sunflower and vegetable oils have their own strengths. Let’s explore their nutritional differences.
Sunflower Oil: The Antioxidant Champion
Sunflower oil stands out for its high vitamin E content. Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that shields your body from harmful free radicals. Additionally, sunflower oil may boast anti-inflammatory properties and contribute to healthy skin.
Vegetable Oil: A Mix of Benefits
Vegetable oil is a blend of various plant-based oils commonly derived from sources like soybeans, rapeseed, and sunflower seeds. The specific nutritional profile depends on the exact blend used. Generally, vegetable oil tends to be higher in omega-6 fatty acids. These are essential for healthy skin and brain function.
Moderation is Key
While omega-6 fatty acids are important, consuming too much can disrupt the balance of omega-3 fatty acids in your body. This is why moderation is key for both sunflower and vegetable oil. Use them in balanced portions as part of a healthy diet.
In Summary
Both sunflower and vegetable oils offer distinct nutritional advantages. Sunflower oil shines with its vitamin E content, while vegetable oil provides a good source of omega-6 fatty acids. Remember, moderation is crucial. Enjoy these oils as part of your balanced diet!
Choosing Between Sunflower Oil and Vegetable Oil

When it comes to cooking oils, sunflower and vegetable oil are popular choices. Both offer unique benefits and considerations.
- Sunflower Oil: Rich in vitamin E and potentially anti-inflammatory, sunflower oil is excellent for skin health. It boasts a high smoke point, making it ideal for deep frying and high-heat cooking. Additionally, its neutral flavor allows other ingredients to shine.
- Vegetable Oil: This versatile option comes from various plant sources, offering a wider range of flavors depending on the specific blend. Vegetable oil is a good source of essential omega-6 fatty acids.
Making the Right Choice
The best oil depends on your specific needs and preferences. Here are some factors to consider:
- Cooking Method: Sunflower oil has a high smoke point, making it suitable for deep frying or high-heat cooking. Vegetable oil offers more flexibility for various cooking styles.
- Flavor: Sunflower oil is neutral, while vegetable oil’s flavor can vary depending on the blend. Use this to your advantage!
- Nutrition: Both oils are similar, but sunflower oil has more vitamin E and a healthier fat composition.
- Health Concerns: If you have nut allergies, vegetable oil (often a blend) might be a safer option than some nut-based oils.
Ultimately, the best oil is the one that best suits your needs, taste preferences, and health goals. Experiment with both to find what elevates your dishes!
References:
- https://time.com/5342337/best-worst-cooking-oils-for-your-health/
- https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-difference-between-vegetable-oil-and-sunflower-oil-Can-you-have-both-at-once-in-your-kitchen
FAQ About Oil Showdown: Sunflower Oil Vs Vegetable Oil
Q: What is the primary difference between sunflower oil and vegetable oil?
A: The main difference lies in their sources. Sunflower oil is extracted from sunflower seeds, while vegetable oil is a generic term that may refer to various plant-based oils like soybean, canola, or corn oil.
Q: Which oil is healthier, sunflower oil or vegetable oil?
A: Both oils have their own health benefits. Sunflower oil is rich in vitamin E and low in saturated fats, while vegetable oil, depending on the type, may offer different nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids. It’s essential to consider your dietary needs when choosing between the two.
Q: Can sunflower oil and vegetable oil be used interchangeably in cooking?
A: Yes, both oils can typically be used interchangeably in most recipes. However, they may impart slightly different flavors, so it’s best to use them based on the specific taste you want to achieve.
Q: Are there any differences in smoke points between sunflower oil and vegetable oil?
A: Sunflower oil generally has a higher smoke point compared to most vegetable oils, making it a better option for high-heat cooking methods like frying. However, specific types of vegetable oils, such as avocado oil, might have comparable smoke points to sunflower oil.
Q: Which oil is more suitable for salad dressings, sunflower oil or vegetable oil?
A: Sunflower oil is known for its mild flavor, making it a good choice for salad dressings as it won’t overpower other ingredients. Vegetable oils, especially those with neutral flavors like canola oil, can also work well in salad dressings. Consider your taste preferences when making your selection.

The Finer Diner has a rich history deeply rooted in the Mt. Oliver and Hilltop community. Our journey began with a simple yet ambitious vision – to create a welcoming space where friends and families could come together to enjoy delicious, comforting meals in a classic diner-style setting. Since our establishment, we have been dedicated to serving food, creating lasting memories, and fostering a sense of belonging within our community. Our commitment to quality, authenticity, and exceptional service has been the cornerstone of our success.